“Prototyping is the conversation you have with your ideas.” – Tom Wujec
For any project to be successful and meet customer demands to the tee, is most important and sometimes, most difficult too. Going by the past standards, customers tested the projects only almost after they were through the development and unit testing phase. Even if they were involved during the early phases, there was no model before them that could give them an idea of what they were going to get, in the future to come. That is where the concept of prototyping came in and now, is a part and parcel of almost all implementations.
In the modernized era today, creating a prototype of your project can be a crucial factor in the success or failure of the project. A prototype, as a preliminary version of the product, can help users visualize how the project will look and behave. It can be of the finest importance to the end customer as well as your team, in terms of understanding the loopholes and coming up with a seamless product at the end.
Rapid prototyping is the new normal today, that offers the best prototyping techniques. It is being adapted by organizations, worldwide, thanks to its salient features. This write-up talks everything about Rapid Prototyping, its key features, benefits, and the future thereafter.
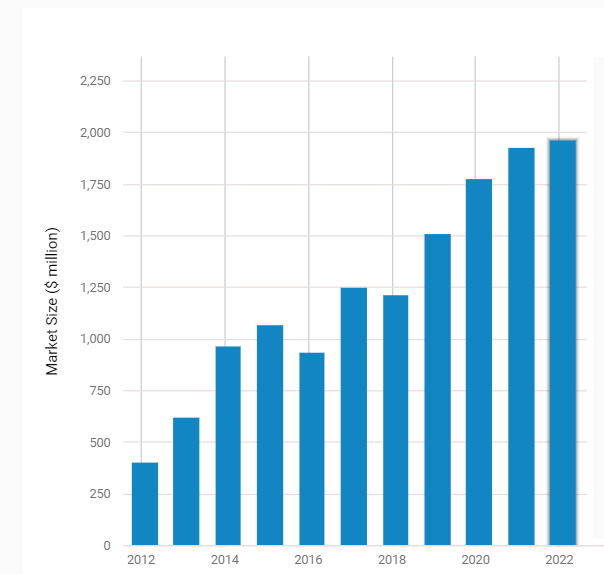
Courtesy: 3D Printing & Rapid Prototyping Services in the US – Market Size 2005–2027
What is Rapid Prototyping? An Overview
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or “additive layer manufacturing” technology. – Wikipedia
Rapid Prototyping showcases a method that empowers organizations to come up with a prototype right at the beginning of the project. It enables users to find out loopholes in a timely fashion, lessening extra expenses that could incur because of the errors. The main objective behind this technique is to convert ideas into quantifiable prototypes as early as possible with thorough testing by the client.
This methodology is implemented with the help of 3D computer-aided design. It is ideally meant for engineers and manufacturers who are looking to get their designs tested and verified before it reaches the customer. Ideally, it is used at the start of the project but if needed, a rapid prototype can be created at any stage of the project. It can even be repeated multiple times to finally get the preferred result. It creates a physical output directly from its CAD-based data with the help of different processes.
Rapid Prototyping is
- Creating a prototype for a visual and functional evaluation of a part or feature
- Quick fabrication of a physical component with 3D CAD called 3D printing
- Meant for fast evaluation, testing, and analysis of any project
- Performed with additive manufacturing, casting, molding, high-speed machining, etc.
The different stages that are involved in a Rapid Prototype development are:
- Conceptualizing all ideas together with possible outcomes
- Designing all identified components with components like buttons, animations, etc.
- Developing all involved parts of the project with relevant dependencies
- Testing all possible scenarios with different test cases and test data
The possible Rapid Prototyping types are:
- Functional prototypes
- Visual prototypes
- Pre-production/production prototypes
- Moulds for prototyping
- Conceptual models
Rapid Prototyping can be applied in areas like the creation of drones, development of defense machinery, medical devices, and automotive parts, and in industry segments like manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, consumer goods and electronics, aerospace, etc.
Rapid Prototyping can be done through different techniques like Selective laser sintering (SLS), Stereolithography (SLA), Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), Binder jetting, Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), Poly jetting.
Good Read: MVP Vs Prototype Vs POC – A Complex Choice of Strategy Made Simple
How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
Below mentioned are the main steps that are taken, while going through the process of Rapid Prototyping:
- Picking up a virtual design through modeling or CAD software
- Reading of data by the 3D machine from the CAD drawing with additive manufacturing
- Usage of standardized STL file format for translation from CAD to 3D machine
- Laying down of relevant material to create the physical model from different sections
- Joining the different sections together to create the final prototype
Salient Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
- Offers a comprehensive, precise, and detailed view of how the product will look and operate, with effective communication with the customer
- Facilitates any type of changes, updates, and enhancements in the early stages of the project, saving time, money, and efforts
- Increases the chances of an easy acceptance by the customer in the final implementation stages
- Since it is an automated process, it does not need too many resources to operate. Hence, it can be easily done with limited resources.
- Encourages designers to come up with innovative designs, experiments, and ideas that can be incorporated firstly in the prototype and in the final design, if successful
- Being an integrated method, it helps client needs to be easily incorporated into the main design components
- Offers a larger choice spectrum and a flexible approach for clients
- Helps in reducing documentation by replacing text with actual workable prototypes
- Replaces months of wait time to faster results in days/week, with a reduction in time-to-market
- Creates enhanced, competitive, and better performing models with each build of prototype
- Easy sharing of ideas and fundamentals with clients and other taskforce members
- Lessens chances of errors in the design components
- Increased involvement of end users during early stages of development
An Example of Rapid Prototyping
A very frequent example of the above is 3D printing. In usual cases, many understand 3D printing as a synonym of Rapid Prototyping, such routinely it is used. Faster 3D models can be constructed with this print variant, and it can bring about a lot of time and cost savings during the entire production session. There are other ways of doing this – videos, sketches, etc. but 3D printing is the most routinely used.
Challenges Faced During Rapid Prototyping
However rewarding it may look, there are certain hurdles that are attached to a Rapid Prototype implementation. Of course, they can be handled and managed with appropriate actions. Here are they:
- Cost and supply of equipment in a timely manner
- The expenditure involved in the post-production and pre-production stages
- Capability to cater to in-house additive manufacturing processes
- Lack of recognized standards and accuracy
- A dearth of skilled and trained resources
Till Later
So right said by Tom & David Kelly – ‘If a picture is worth 1000 words, a prototype is worth 1000 meetings.’ Rapid Prototyping works best for creating a replica of what you desire, fastening your work processes, go-to-market time, and reducing the chances of getting a rejection by the customer.
It has a bright future, some of the futuristic trends show great happenings. Some of them are Rapid Prototyping with AI, autonomous driving development, creation of physical 3D maps and website services for 3D models covered by maps, GPS tracks, satellite images etc.
Rapid Prototyping is revolutionizing the business world, especially the manufacturing domain. It is interesting to watch the IT world fuse with our daily business activities and bring about a great revolution! The unbelievable is yet to come!