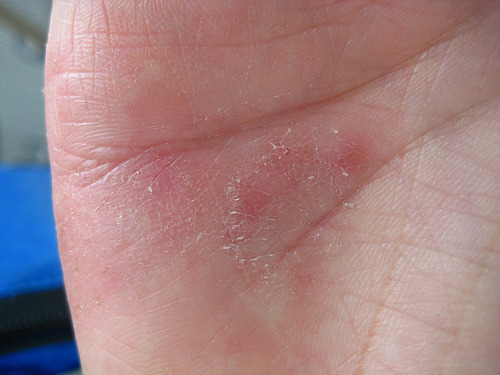
<p style="text-align: justify">Eczema is a general term used to describe several different skin conditions that cause color changes, dryness, inflammation and discomfort. However, not all of these conditions are the same, and treatment options vary. Below is some information about the causes, symptoms and treatment options for three common types of eczema.</p>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Atopic Dermatitis</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">According to the National Eczema Society, atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. This condition affects both children and adults. Causes of atopic dermatitis vary, but may include genetic factors, dry skin and environmental conditions and problems with the immune system.</p>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Symptoms</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">The signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Flaky dry skin on elbow or knees</li>
<li>Redness</li>
<li>Scaling</li>
<li>Itching</li>
<li>Oozing</li>
<li>Weeping</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: justify">In infants, other symptoms may include trouble sleeping and rubbing of the infected areas on rough surfaces to relieve the itch. Atopic dermatitis is most common in infants and children. However, some people may retain the symptoms of atopic dermatitis into adulthood. It is rare for atopic dermatitis to begin in adulthood.</p>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Treatment</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">There is no cure for atopic dermatitis, and treatments typically focus on reducing the symptoms. Treatments for atopic dermatitis may include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Antihistamines</li>
<li>Corticosteroids</li>
<li>Moisturizers</li>
<li>Phototherapy</li>
</ul>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Contact Dermatitis</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema that occurs when the skin comes into contact with certain irritants. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, irritants that may cause contact dermatitis include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Latex</li>
<li>Makeup</li>
<li>Jewelry</li>
<li>Fragrances</li>
<li>Prolonged contact with water</li>
<li>Chemicals</li>
<li>Coarse fabrics</li>
<li>Certain soaps</li>
</ul>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Symptoms</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">Signs and symptoms of contact dermatitis include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Fluid-filled blisters</li>
<li>Crusting and scaling</li>
<li>Itching</li>
<li>Hives</li>
<li>Burning and stinging</li>
<li>Excessive dryness</li>
<li>Swelling and redness</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: justify">If the irritation continues, your skin may thicken and become leathery, scaly, flaked or cracked. Sometimes your skin can become so cracked and irritated that it will scab, produce pus or bleed.</p>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Treatment</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">Before you can treat contact dermatitis, you must find out which irritants are causing the reaction. In some cases, it may be obvious. However, if you aren&#8217;t sure, a dermatologist can test your skin to determine which substances cause a reaction. After you know the source of the problem, you can reduce the symptoms by simply avoiding it. Treatments for existing rashes may include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Corticosteroids</li>
<li>Antihistamines</li>
<li>Moisturizers</li>
<li>Oral steroids</li>
</ul>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Seborrhoeic Eczema/Dermatitis</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">Seborrhoeic eczema can affect both children and adults. In children, it may also be called &#8220;cradle cap.&#8221; The main area affected is the scalp, but it may also spread to the ears, eyebrows, neck, temples and other locations on the body. Although the cause of this condition isn&#8217;t always clear, the National Eczema Society reports that many people with seborrhoeic dermatitis have an overgrowth of a fungus known as pityrosporum ovale.</p>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Symptoms</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">Signs and symptoms of seborrhoeic dermatitis include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Inflamed skin</li>
<li>Itching</li>
<li>Yellowish scales or flakes</li>
</ul>
<h2 style="text-align: justify"><strong>Treatment</strong></h2>
<p style="text-align: justify">Seborrhoeic dermatitis is difficult to cure and often recurs when treatment is stopped. Treatments for this condition include:</p>
<ul style="text-align: justify">
<li>Antifungal shampoo</li>
<li>Antifungal medication</li>
<li>Corticosteroids</li>
<li>Phototherapy</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: justify">Most forms of eczema respond well to treatment. If you have symptoms of any of the conditions listed above, consult your dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment options.</p>
<p style="text-align: justify">+Dr.Cheryl Lee has developed a sensitive skin care product line which she blogs about regularly at cherlyleemd.com</p>

3 Different Types Of Eczema